The KY-026 module is a flame detection circuit board that uses a YG1006 sensor. It can detect infrared light emitted from the surroundings in the event of a fire and works with microcontrollers like Arduino, Raspberry Pi, and ESP32. The module has both digital and analog outputs. The digital output acts like a switch that turns on when a flame is detected, while the analog output can measure the intensity levels of the flame. It features an onboard potentiometer to adjust the sensitivity of flame sensing.
KY-026 Flame Sensor Module Specifications
The quick specifications of this sensor module is given below:
- Module: Flame Sensor
- Type: Analog/Digital
- Main Chips: LM393, Y1G1006
- Pin Connector to board: 4 Pins
- Operating Voltage: DC +3.3V to +5V
- Infrared Wavelength Detection: 760 nm to 1100 nm
- Sensor Detection Angle: 60°
- PCB Color: Red
- Board Dimensions (L x W x H): 36 x 15 x 10 mm
- Weight: 3gm
Pinout of KY-026 Flame Sensor Module
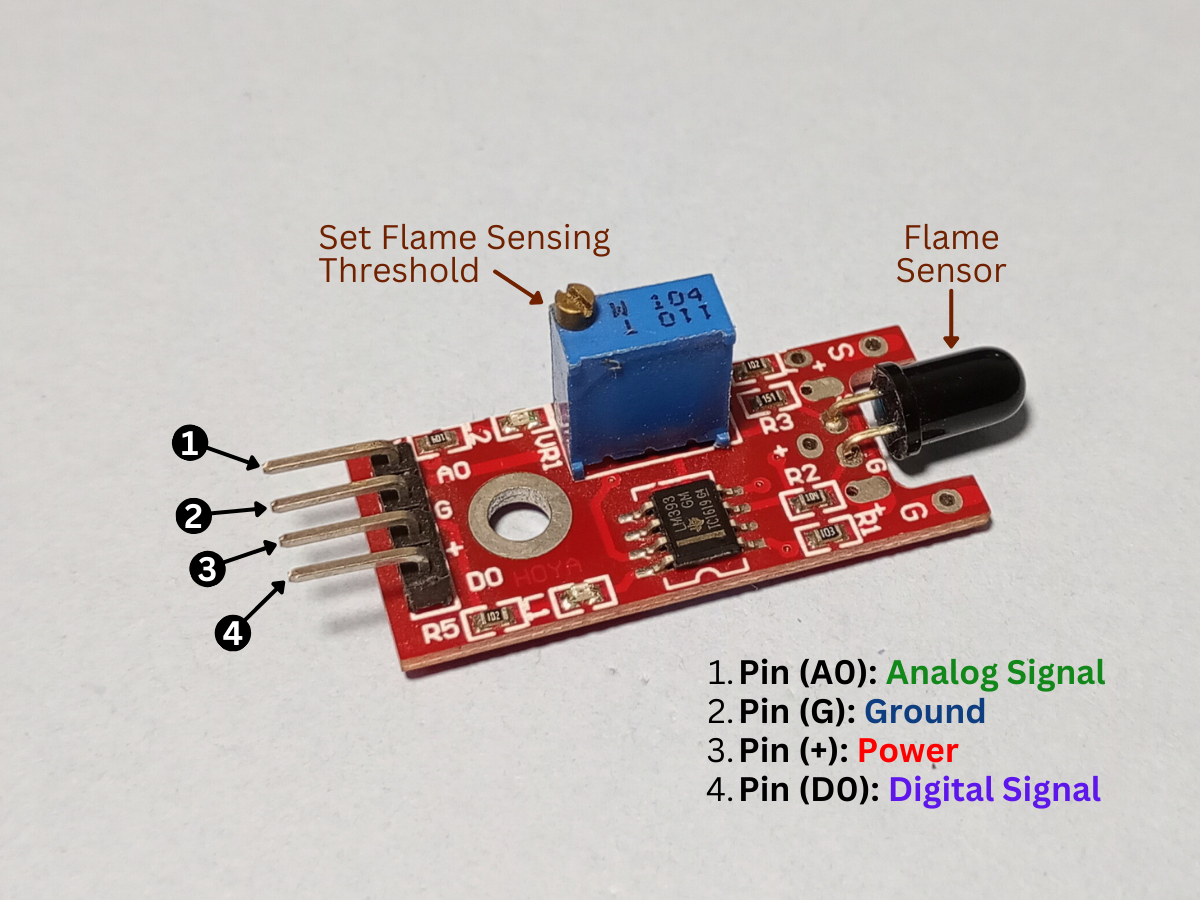
|
The module has 4 male header pins those are -
|
Working Explanation of KY-026 Flame Sensor Module Circuit
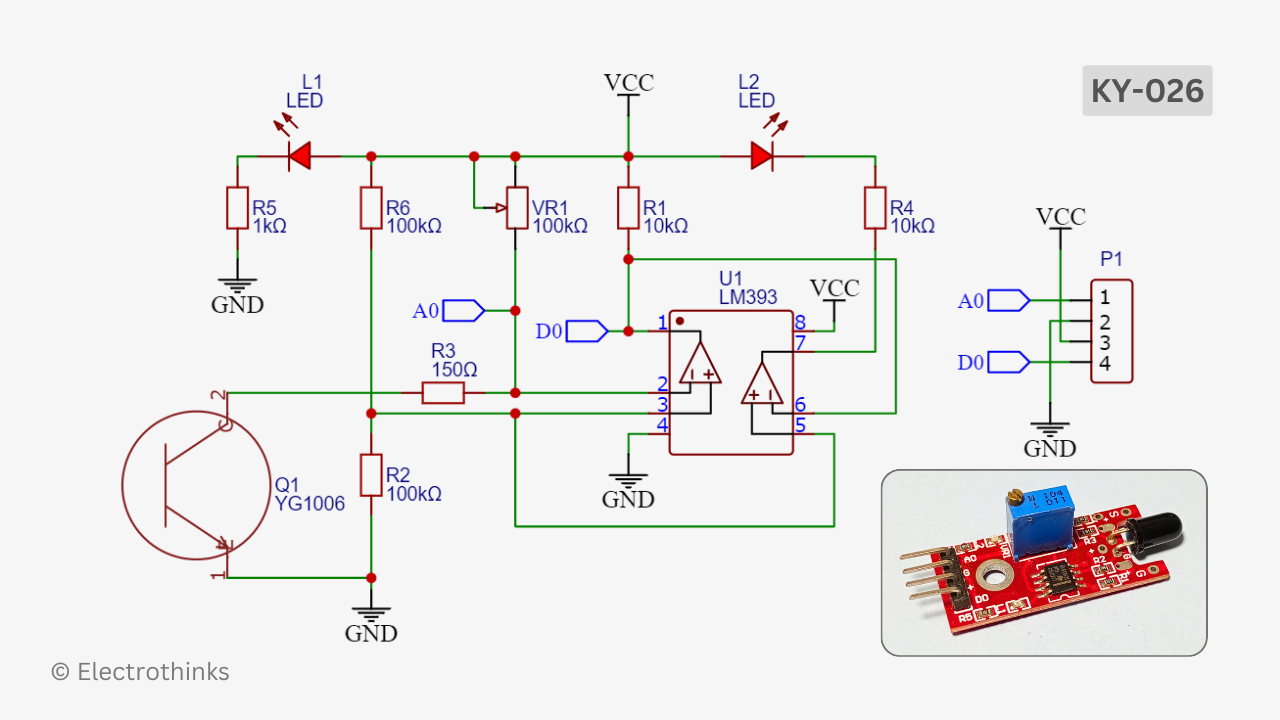
Schematic of the KY-026 flame sensor module circuit is shown below.
Components are used in the circuit - U1: IC LM393, Q1: 5mm IR Diode - YG1006, VR1: 100kΩ Multiturn Potentiometer, R1 & R4: 10kΩ, R2 & R6: 100kΩ, R3: 150Ω, R5: 1kΩ, L1 & L2: Red LED, and P1: 4 pin Male header.
The module integrates both analog and digital circuits designed to operate within a voltage range of 3.3-5V DC. It has an LED (L1) to indicate the power supply status through blinking.
The YG1006 IR sensor, like all other photosensors, works on the principle that a photon of sufficient energy can knock out electrons, changing the resistance of the circuit.
When the IR sensor flame detects flame, it allows a flow of current through a potentiometer (VR1) and a resistor (R3) to the ground. The combination of the potentiometer (VR1) and the resistor (R3) acts as a voltage divider, producing a reference voltage. This reference voltage is then taken as the analog signal output (A0) of the circuit, and the sensitivity of the flame detection can be adjusted by the Multiturn potentiometer (VR1).
An LM393 dual comparator IC (U1) is utilized in the circuit for digital functions, which contains two comparators. The analog signal output from the voltage divider (VR1 and R3) is fed into the inverting input (pin-2) of the first comparator, while a fixed reference voltage from a second voltage divider (R2 and R6) is connected to the non-inverting input (pin-3) of the same comparator.
When a certain level of flame (760nm ~ 1100nm) is detected and current flows through the IR (Q1) to ground, the reference voltage across the voltage divider (VR1 and R3) decreases. If this voltage drops below the reference voltage from the voltage divider (R2 and R6) at the non-inverting input of the first comparator, the output at pin-1 goes high.
The output from the first comparator is connected to a pull-up resistor (R1), ensuring a defined logic level for the output signal (D0). This high signal from the first comparator is also sent to the non-inverting input (pin-6) of the second comparator, while the reference voltage from the voltage divider (R2 and R6) is connected to the inverting input (pin-7) of the second comparator.
When the first comparator outputs a high signal in response to the detected sound, the second comparator checks if this high signal exceeds the reference voltage from the divider (R2 and R6). If the signal from the first comparator is greater than the reference voltage, the second comparator outputs a low signal at its output (pin-6). This low signal causes the LED (L2) to blink.
Interfacing KY-026 module with Arduino
| Connection diagram of the KY-026 Flame sensor module. |
KY-026 module Arduino Example Code
int led = 13; // initializing pin 13 as the LED pin
int digitalPin = 2; // initializing pin 2 as KY-026 digital interface
int analogPin = A0; // initializing pin A0 as KY-026 analog interface
int digitalVal; // state of digital readings
int analogVal; // state of analog readings
void setup()
{
pinMode(led, OUTPUT);
pinMode(digitalPin, INPUT);
//pinMode(analogPin, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop()
{
// Read the digital interface
digitalVal = digitalRead(digitalPin);
if(digitalVal == HIGH) // if flame is detected
{
digitalWrite(led, HIGH); // turn ON Arduino's LED if a flame is detected
}
else
{
digitalWrite(led, LOW); // otherwise turn OFF Arduino's LED
}
// Read the analog interface
analogVal = analogRead(analogPin);
Serial.println(analogVal); // print analog value to serial
delay(100);
}







Good circuit diagram.
ReplyDeleteWhere did you make connection diagram?
ReplyDelete